Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Tadashi; Kondo, Masaya
JSME International Journal, Series B, 49(2), p.296 - 301, 2006/05
no abstracts in English
Weisenburger, A.*; Aoto, Kazumi; M ller, G.*; Heinzel, A.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro
ller, G.*; Heinzel, A.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/06
The behaviour of protective oxide layers on P122 and its welds and of ODS steel in LBE is examined under conditions of changing temperatures and oxygen concentrations. P122 teel ( Cr) and its welded joints are exposed to LBE at 550
Cr) and its welded joints are exposed to LBE at 550  C for 4.000 h with oxygen concentrations of 10
C for 4.000 h with oxygen concentrations of 10 and 10
and 10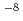 wt% which change every 800 h. It is found that like in case f constant oxygen concentration of 10
wt% which change every 800 h. It is found that like in case f constant oxygen concentration of 10 wt% a protective spinel layer was maintained on P122 and also on its welded joint. Two experiments are conducted on ODS steel, both with temperatures changing from 550 to 650
wt% a protective spinel layer was maintained on P122 and also on its welded joint. Two experiments are conducted on ODS steel, both with temperatures changing from 550 to 650  C and back every 800 h, one experiment with 10
C and back every 800 h, one experiment with 10 the other with 10
the other with 10 wt% oxygen in LBE. Like in the former test with constant emperature at 550
wt% oxygen in LBE. Like in the former test with constant emperature at 550  C no dissolution attack could be observed in experiments with temperature fluctuation. Contrary to this results is the observed dissolution attack on ODS with a onstant temperature of 650
C no dissolution attack could be observed in experiments with temperature fluctuation. Contrary to this results is the observed dissolution attack on ODS with a onstant temperature of 650  C at 10
C at 10 wt% oxygen in which formation of a protective layer was not allowed before reaching 650
wt% oxygen in which formation of a protective layer was not allowed before reaching 650  C LBE temperature.
C LBE temperature.
Kotake, Shoji; Namba, Takashi; Sagayama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
None
Kotake, Shoji; Namba, Takashi; Sagayama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
None
Sakamoto, Yoshihiko; Kotake, Shoji; Nishikawa, Akira; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ando, Masato; Sagayama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
The Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor (FR) Cycle Systems is under way in order to propose prominent FR cycle systems that will respond to the diverse needs of society in the future. The design studies on various FR system concepts have been achieved and then the evaluations of potential to achieve the development targets have been carried out. Crucial issues have been found out for each FR system concept and their development plans for the key technologies are summarized as the roadmap. The characteristics and the differences in performances have been investigated. The crucial issues and the development periods have been clarified. Further investigation is now in progress. The promising concept will be proposed based on result of comparative evaluation at the end of the Phase II study.
Sotsu, Masutake; Yamada, Fumiaki*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
MONJU is a sodium cooled, loop-type prototype fast breeder reactor which can supply 280MW of electricity to the grid. The generated heat at the reactor core is removed by three loops of primary heat transport system (PHTS), each of those is thermally connected through individual intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) to another clloant eirculation loop of secondary heat transport system (SHTS). The turbine generator is driven by steam generated at three evaporators and super heaters installed at the SHTS.
Abe, Tomoyuki; Maeda, Seiichiro; Nakazawa, Hiroaki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) developed plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) fuels for an advanced thermal reactor (ATR) for a flexible utilization of plutonium. JNC made endeavors to obtain well-homogenized MOX pellets by a ball mill mixing method with a variety of raw powders, including MOX powder by a microwave-heating denitration process. A total of 772 MOX fuel assemblies were utilized in the ATR prototype reactor
Washiya, Tadahiro; Higuchi, Hidetoshi; Sano, Yuichi; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), P. 330, 2005/05
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has been developing the crystallization technology for the advanced aqueous reprocessing plant to realize the FBR fuel cycle. The crystallization process is applied in front of the extraction process for removing large amount of uranium and reducing the throughput of extraction process. The crystallization process requires high concentrated dissolution ( 500g-HM/L) to mitigate the cooling conditions. The powdered fuel dissolution is a promising technology to obtain the high concentrated dissolution. Hot experiments of the powdered fuel dissolution were carried out at CPF to verify the dissolution speed and characteristics. As result, the speed is ten times faster than conventional sheared fuel. For the powdered fuel dissolution, particle handling is a key issue to prevent piling up of the fuel particles on the dissolver bottom and elutriation rate to the off gas system. In this paper, functional requirements and subjects for the powdered fuel dissolution were discussed. And an innovative dissolver design based on the cylindrical stirring type dissolver was proposed for reliable continuous dissolver system with the powdered fuel. Some engineering scale test and computer code evaluations were carried out to verify the dynamic performance of simulated fuel particles and water in the dissolver design.
500g-HM/L) to mitigate the cooling conditions. The powdered fuel dissolution is a promising technology to obtain the high concentrated dissolution. Hot experiments of the powdered fuel dissolution were carried out at CPF to verify the dissolution speed and characteristics. As result, the speed is ten times faster than conventional sheared fuel. For the powdered fuel dissolution, particle handling is a key issue to prevent piling up of the fuel particles on the dissolver bottom and elutriation rate to the off gas system. In this paper, functional requirements and subjects for the powdered fuel dissolution were discussed. And an innovative dissolver design based on the cylindrical stirring type dissolver was proposed for reliable continuous dissolver system with the powdered fuel. Some engineering scale test and computer code evaluations were carried out to verify the dynamic performance of simulated fuel particles and water in the dissolver design.
Takamatsu, Misao; Sekine, Takashi; Uchita, Masato*; Harada, Kiyoshi*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Self actuated shutdown system (SASS) with a Curie point electromagnet (CPEM) is being developed for use in a large scale fast breeder reactor (FBR) in order to establish the passive shutdown capability against anticipated transient without scram (ATWS) events. In order to confirm the stability of CPEM in holding the control rod and demonstrate the functions of the driving system to re-connect and pull out the control rod under the actual reactor-operational environment, the component function test using the reduced-scale model experimental equipment of SASS was conducted in the experimental fast reactor JOYO MK-III. As a result of this test conducted for 117 days during the 1st and 2nd operational cycles of JOYO MK-III from May to Oct. 2004, the rod-holding stability and the recovering functions of the driving system were fully confirmed. A neutron fluence of over 6 1018n/cm2 (E
1018n/cm2 (E 0.1MeV) was obtained for CPEM. This corresponded to 60 years of use in a large-scale FBR and satisfied the required fluence for stability assurance. The results also will likely dispel the apprehensiveness about the operational trouble involving the unexpected drop of SASS.
0.1MeV) was obtained for CPEM. This corresponded to 60 years of use in a large-scale FBR and satisfied the required fluence for stability assurance. The results also will likely dispel the apprehensiveness about the operational trouble involving the unexpected drop of SASS.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Konys, J.*; M ller, G.*; Aoto, Kazumi
ller, G.*; Aoto, Kazumi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Two kind of high chromium martensitic steels named as 12Cr-steel and ODS-M, proposed for use in fast breeder reactors were subjected to corrosion tests in flowing lead bismuth eutectic (LBE) under active oxygen control at 823 K for up to 5,000 hours. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in LBE was controlled by H2/H2O mixture gas bubbling into LBE to keep at 10-6 wt%. However, the oxygen concentration was degreased with increasing of operation time, and temporarily reached below the value necessary for magnetite formation. Then, after 3,300 hours of effective operation time, oxygen concentration was controlled near the target value by periodically adding argon and mixtures of argon and technical air to the H2/H2O mixture gas stream through the oxygen control system. Both steels exposed in LBE under the condition showed approximately the same corrosion behavior. Double-layer structure composed of Fe-Cr spinel and diffusion zone were observed on the surface of the steels exposed for up to 2,000 hours. After 5,000 hours of exposure, it changed to single-structure composed of Fe-Cr spinel. Results of thickness measurement of the oxide layers, the total thickness of oxidized zone was approximately constant during test periods from 800 hours to 5,000 hours. It meant that the steels showed good corrosion resistance under this tested condition. In addition, both erosion and dissolution attack called as liquid metal corrosion were not observed on the all tested specimens.
Fujii, Tadashi; Konomura, Mamoru; Kamide, Hideki; Yamaguchi, Akira; Toda, Mikio*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
An innovative sodium-cooled fast reactor (JSFR) has been investigated on the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor (FR) Cycle Systems. In order to reduce plant construction cost, JSFR adopts compacted reactor vessel and reduction of loop number. According to adoption of compacted cooling system, sodium flow velocities in the reactor upper plenum and the pipings of the cooling system exceed to those of conventional design, therefore, flow optimization in the reactor upper plenum and structural integrity of the piping system to flow-induced vibration (FIV) have been actualized as thermal-hydraulic issues. To solve above issues, some water experiments have been performed. The thermal-hydraulic design of the primary cooling system including the reactor vessel has been advanced reflecting these experimental results.
Ohno, Shuji; P. Loewen, Eric*; Auman, L. E.*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
The alkaline extraction method and electro-deposition method have been investigated at the Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory to remove polonium from a lead-bismuth cooled reactor. Tellurium was used as a surrogate for polonium for these experiments to quantify the migration. From the chemical kinetic measurements of extraction tests using NaOH as alkaline, first and second order alkaline extraction rate constants were suggested to be: k1=300exp(-64300/RT), k2=42700exp(-122400/RT), where R=8.31J/mol/K and T is in degrees K. Some experimental data showed tellurium moving from NaOH back into LBE, allowing the measurement of the reverse rate reaction constant. We suggest the following linear fit to determine the equilibrium constant as a function of the temperature: Log(K)=-3195/T+5.199. The electro-deposition experiments were initiated. The limited number of runs provided the information of the effect of electrodes surface area and temperature on the tellurium collection characteristics. However, further experiments are necessary for acquiring more knowledge. This paper is a continuation of the results reported in the previous ICONE papers: ICONE11-36614 and ICONE12-49396.
Saito, Junichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
The reaction tests between sodium and lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) have been carried out changing test temperature and the amount of LBE as the parameters in order to make clear the reaction behavior. From the experiments, it is elucidated that the temperature of liquid sodium rises immediately by dropping LBE. It shows the exothermic reaction between LBE and liquid sodium. Amounts of dissolution of lead and bismuth in sodium increase when the temperature rise is large. They change depending largely on the temperature of reaction. Many fine reaction products are observed in sodium, and the amount of reaction products depends on the amount of dropped LBE. The dominant reaction product is BiNa which is one of sodium-bismuth binary compounds. A reaction heat calculated from the temperature rise of liquid sodium is comparable to a reaction heat estimated by the standard enthalpy of BiNa
which is one of sodium-bismuth binary compounds. A reaction heat calculated from the temperature rise of liquid sodium is comparable to a reaction heat estimated by the standard enthalpy of BiNa . The reaction behavior between sodium and LBE is clarified on the basis of these experimental results.
. The reaction behavior between sodium and LBE is clarified on the basis of these experimental results.
Seino, Hiroshi; Jitsu, Koji*; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ono, Isao*; Hamada, Hirotsugu
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Blow down analysis code (LEAP-BLOW) and sodium-water reaction jet analysis code (LEAP-JET) have been developed to improve the evaluation accuracy on sodium-water reaction. The validation analyses by these codes were carried out using the data of SWAT-1R test. As the result, though there was a problem in the quantitative evaluation of LEAP-JET, it was possible to obtain the approximately appropriate results.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamaguchi, Akira
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), 0 Pages, 2005/05
Temperature fluctuation caused by the turbulence mixing of different temperature fluids gives thermal fatigue to structure according its amplitude and frequency. This phenomenon is significant as safety issue in liquid metal cooled fast reactor (LMFBR). In Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), experimental and numerical investigations have been carried out to clarify the turbulence mixing phenomena and to establish an evaluation rule for the thermal fatigue in LMFBR. Large-scale eddy motion in turbulence mixing causes the temperature fluctuation with large amplitude and low frequency component. In the estimation of thermal fatigue, heat transfer coefficient under large-scale eddy motion and such a temperature fluctuation are important factors for accurate prediction of thermal stress in the structure. In this study, numerical simulation was carried out to investigate the local heat transfer mechanism under large-scale eddy motion and the treatment of heat transfer coefficient in the transient phenomena was discussed in relation to the thermal fatigue estimation.
Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
no abstracts in English
Miyazaki, Akemi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/05
Since it is generally difficult to predict the occurrence of the natural disasters such as earthquakes, a performance management system that always maintains the safety of the structures is required, especially for the critical ones like the nuclear power plants. To realize such a system, it is becoming important to carry out modeling procedures and analyses in detail to capture the real phenomena. Such details are important in understanding the phenomena occurring in the frame structures such as piping systems which are considered to be one of the most weakest and vulnerable parts in the nuclear power plants. The aim of our research is to solve the dynamic behavior, especially the wave propagation phenomena for the piping systems in the nuclear power. The spectral element method is adopted in this work and the formulation considering a shear deformation of a frame element is described. Timoshenko beam theory is introduced for the purpose of this formulation. The validity of the presented element will be shown through the comparisons made with the conventional beam element.
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
A hydrogen production system connected to the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is being designed to be able to produce hydrogen using a nuclear heat of 10 MW supplied by the HTTR. The HTTR hydrogen production system is first connected to a nuclear reactor in the world, hence an mock-up model test is planned to carry out prior to the demonstration test of the HTTR hydrogen production system. In parallel to the mock-up model test, the following tests as an essential problem, a corrosion test of a reforming tube, a permeation test of hydrogen isotopes through a heat exchanger tube, an integrity test of a high-temperature isolation valve, and a performance test of a hydrogen permselective membrane are carried out to obtain detailed data for a safety review and development of analytical codes. This paper describes the present status of the component tests on the R&D of the HTTR hydrogen production system.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakatsuka, Toru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
In order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the matured Light Water Reactor (LWR) and coming LWR-Mixed Oxide (MOX) technologies, a concept of Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been investigated in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The concept consists of two parts in the chronological sequence. The first part realizes a high conversion type core concept, which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from current LWR without significant gaps in technical point of view. The second part represents the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) core concept, which realizes a high conversion ratio over 1.0 being useful for the long-term sustainable energy supply through plutonium multiple recycling based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system, based flexibly on the fuel cycle circumstances.
 C in HTTR
C in HTTRKawasaki, Kozo; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Tachibana, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshio; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) achieved a coolant temperature of 950 C at reactor outlet with its rated thermal power of 30MW on April 19, 2004. Achievement of the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950
C at reactor outlet with its rated thermal power of 30MW on April 19, 2004. Achievement of the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950 C makes it possible to extend use of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors beyond the field of electric power generation. Not only highly effective power generation with a high-temperature gas turbine system but also hydrogen production from water without emission of carbon dioxide will be possible utilizing the high temperature heat. This report describes the results of the high-temperature test operation of the HTTR.
C makes it possible to extend use of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors beyond the field of electric power generation. Not only highly effective power generation with a high-temperature gas turbine system but also hydrogen production from water without emission of carbon dioxide will be possible utilizing the high temperature heat. This report describes the results of the high-temperature test operation of the HTTR.